一、前言 在微服务的架构中,服务间通常会形成相互依赖的关系,比如现在有三个微服务节点:A,B和C,B为A的消费者,C为B的消费者。假如由于网络波动或者A服务自身故障,导致B调用A服务的线程被挂起进入长时间的等待。在高并发的情况下可能导致B的资源被耗竭随之崩溃,从而导致C服务也不可用。这种连环式的雪崩效应在微服务中较为常见,为了解决这个问题,服务熔断技术应运而出。熔断一词来自电路学,指的是电路在出现短路状况时,“断路器”能够及时地切断故障电路,避免电路过载发热引发火灾。
类似的,微服务架构中的断路器能够及时地发现故障服务,并向服务调用方返回错误响应,而不是长时间的等待。Spring Cloud Hystrix在Hystrix(又是一款由Netflix开发的开源软件,Github地址 https://github.com/Netflix/Hystrix 的基础上进行了封装,提供了服务熔断,服务降级,线程隔离等功能,通过这些功能可以提供服务的容错率。
二、介绍 2.1 请求熔断 断路器是一种开关设置,当某个服务单元发生故障之后,通过断路器的故障监控,向调用方返回一个符合预期的服务降级处理(fallback),而不是长时间的等待或者抛出调用方无法处理的异常,这样保证了服务调用方的线程不会长时间被占用,从而避免了故障在分布式系统的蔓延乃至崩溃。
2.2 服务降级 fallback 相当于是降级操作。对于查询操作, 我们可以实现一个 fallback 方法, 当请求后端服务出现异常的时候, 可以使用 fallback 方法返回的值。 fallback 方法的返回值一般是设置的默认值或者来自缓存,告知后面的请求服务不可用了,不要再请求了。
2.3 请求熔断和服务降级区别 2.3.1 相同点 1>目标一致:为了防止系统崩溃而实施的一种防御手段
2.3.2 不同 1>触发条件不同:下游服务出现故障触发请求熔断。系统负荷超过阈值触发服务降级。
三、请求熔断实战 本次测试案例基于之前发表的文章中介绍的案例进行演示,不清楚的读者请先转移至 《Spring Cloud Feign声明式服务调用》 进行浏览。
现在的项目列表如下:
项目 服务实例 实例id 端口 描述 common-api 无 无 无 公用的 api,如:实体类 eureka-server Eureka-Server eureka-server1 9001 注册中心(Eureka 服务端) eureka-server Eureka-Server eureka-server2 9002 注册中心(Eureka 服务端) goods-server Goods-Server goods-server1 8801 商品服务(Eureka 客户端) goods-server Goods-Server goods-server2 8802 商品服务(Eureka 客户端) goods-server Goods-Server goods-server3 8803 商品服务(Eureka 客户端) order-server Order-Web order-web 8900 订单服务(Eureka 客户端)
3.1 common-api 3.1.1 增加Goods实体 Goods.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 @Data @NoArgsConstructor @AllArgsConstructor @ToString public class Goods implements Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = -8143412915723961377L; private String goodsId; private String name; private String descr; // 测试端口 private int port; private String instanceId; }
3.1.2 增加Order实体 Order.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 @Data @NoArgsConstructor @AllArgsConstructor @ToString public class Order implements Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = -8143412915723961379L; private String orderId; private String goodsId; private int num; }
3.1.3 增加Result实体 Result.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 @Getter @ToString public class Result implements Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = -8143412915723961323L; private int code; private String msg; private Object data; private Result() {} private Result(int code, String msg) { this.code = code; this.msg = msg; } private Result(int code, String msg, Object data) { this.code = code; this.msg = msg; this.data = data; } public static Result success() { return success(null); } public static Result success(Object data) { return new Result(200, "success", data); } public static Result fail() { return fail(500, "fail"); } public static Result fail(int code, String message) { return new Result(code, message); } }
3.2 goods-server 3.2.1 服务配置 新建一个eureka客户端,创建三个application-xxx.yml
application-goodsserver01.yml
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 server: port: 8801 spring: application: name: Goods-Server eureka: instance: instance-id: goods-server1 prefer-ip-address: off client: register-with-eureka: true # 是否向注册中心注册自己 fetch-registry: true # 是否检索服务 service-url: defaultZone: http://eureka01:9001/eureka/,http://eureka02:9002/eureka/
application-goodsserver02.yml
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 server: port: 8802 spring: application: name: Goods-Server eureka: instance: instance-id: goods-server2 prefer-ip-address: off client: register-with-eureka: true # 是否向注册中心注册自己 fetch-registry: true # 是否检索服务 service-url: defaultZone: http://eureka01:9001/eureka/,http://eureka02:9002/eureka/
application-goodsserver03.yml
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 server: port: 8803 spring: application: name: Goods-Server eureka: instance: instance-id: goods-server3 prefer-ip-address: off client: register-with-eureka: true # 是否向注册中心注册自己 fetch-registry: true # 是否检索服务 service-url: defaultZone: http://eureka01:9001/eureka/,http://eureka02:9002/eureka/
分别对应的service和启动参数如下:
service 启动参数 GoodsServerApplication-goodsserver01-8801 spring.profiles.active=goodsserver01 GoodsServerApplication-goodsserver02-8802 spring.profiles.active=goodsserver02 GoodsServerApplication-goodsserver03-8803 spring.profiles.active=goodsserver03
3.2.2 创建Service GoodsService.java
1 2 3 public interface GoodsService { Goods findGoodsById(String goodsId) ; }
具体实现GoodsServiceImpl.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 @Service public class GoodsServiceImpl implements GoodsService { @Value("${eureka.instance.instance-id}") private String instanceId; @Value("${server.port}") private int port; // 模拟数据库 private static Map<String, Goods> data; static { data = new HashMap<>(); data.put("1", new Goods("1", "手机", "国产手机", 0,"")); data.put("2", new Goods("2", "电脑", "台式电脑", 0,"")); } @Override public Goods findGoodsById(String goodsId) { Goods goods = data.get(goodsId); if (goods == null) { throw new RuntimeException("商品不存在"); } goods.setPort(port); goods.setInstanceId(instanceId); return goods; } }
3.2.3 创建Controller GoodsController.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 @RestController @RequestMapping("/goods") public class GoodsController { @Autowired private GoodsService goodsService; @RequestMapping("/goodsInfo/{goodsId}") public Result goodsInfo(@PathVariable String goodsId) { Goods goods = this.goodsService.findGoodsById(goodsId); return Result.success(goods); } }
3.2 order-server 新建一个eureka客户端
3.2.1 引入依赖 1 2 3 4 <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-hystrix</artifactId> </dependency>
3.2.2 创建Server OrderService.java
1 2 3 public interface OrderService { Result placeOrder(Order order) throws Exception; }
3.3.3 创建Controller 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 @RestController @RequestMapping("/order") public class OrderController { @Autowired private OrderService orderService; @RequestMapping("/place") public Result placeOrder(Order order) throws Exception { this.orderService.placeOrder(order); return Result.success(); } }
3.4 设置熔断策略 编写OrderService具体实现类OrderServiceImpl.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 @Service public class OrderServiceImpl implements OrderService { @Autowired private RestTemplate restTemplate; @HystrixCommand(fallbackMethod = "defaultByPlaceOrder") @Override public Result placeOrder(Order order) throws Exception { Result result = this.restTemplate.getForObject("http://GOODS-SERVER/goods/goodsInfo/" + order.getGoodsId(), Result.class); if (result != null && result.getCode() == 200) { System.out.println("=====下订单===="); System.out.println(result.getData()); } else { System.out.println(result.getMsg()); } return result; } public Result defaultByPlaceOrder(Order order) { System.out.println("商品服务系统异常"); return Result.fail(500, "商品服务系统出现异常,请联系管理员"); } }
当调用商品服务超时或出现异常时,Hystrix 会调用 @HystrixCommand 中指定的 fallbackMethod 方法获取返回值或执行异常处理。
注意:fallbackMethod 方法要求与正常方法有相同的入参和回参。
3.5 启动熔断功能 在启动类上添加@EnableHystrix或者@EnableCircuitBreaker注解,这两个注解是等价的,查看@EnableHystrix注解源码就可以证实这一点:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 @Target({ElementType.TYPE}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Inherited @EnableCircuitBreaker public @interface EnableHystrix { }
在引入@EnableHystrix或者@EnableCircuitBreaker注解后,我们的入口类代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 @EnableHystrix @EnableEurekaClient @SpringBootApplication public class OrderServerApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(OrderServerApplication.class, args); } }
入口类上总共包含了三个注解@EnableCircuitBreaker、@EnableDiscoveryClient和@SpringBootApplication,这三个注解的组合可以使用@SpringCloudApplication来代替,@SpringCloudApplication源码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 @Target({ElementType.TYPE}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Inherited @SpringBootApplication @EnableDiscoveryClient @EnableCircuitBreaker public @interface SpringCloudApplication { }
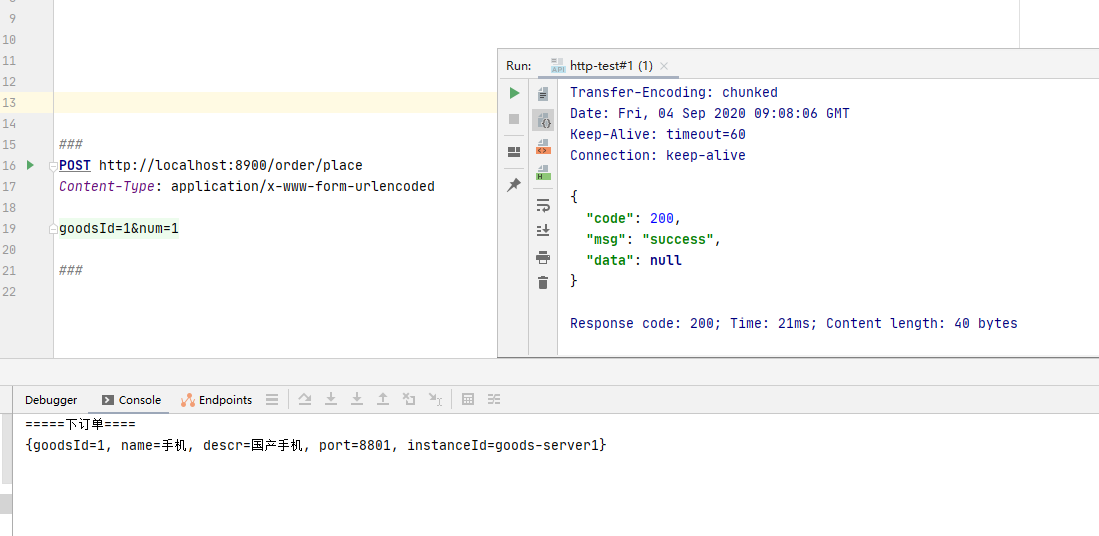
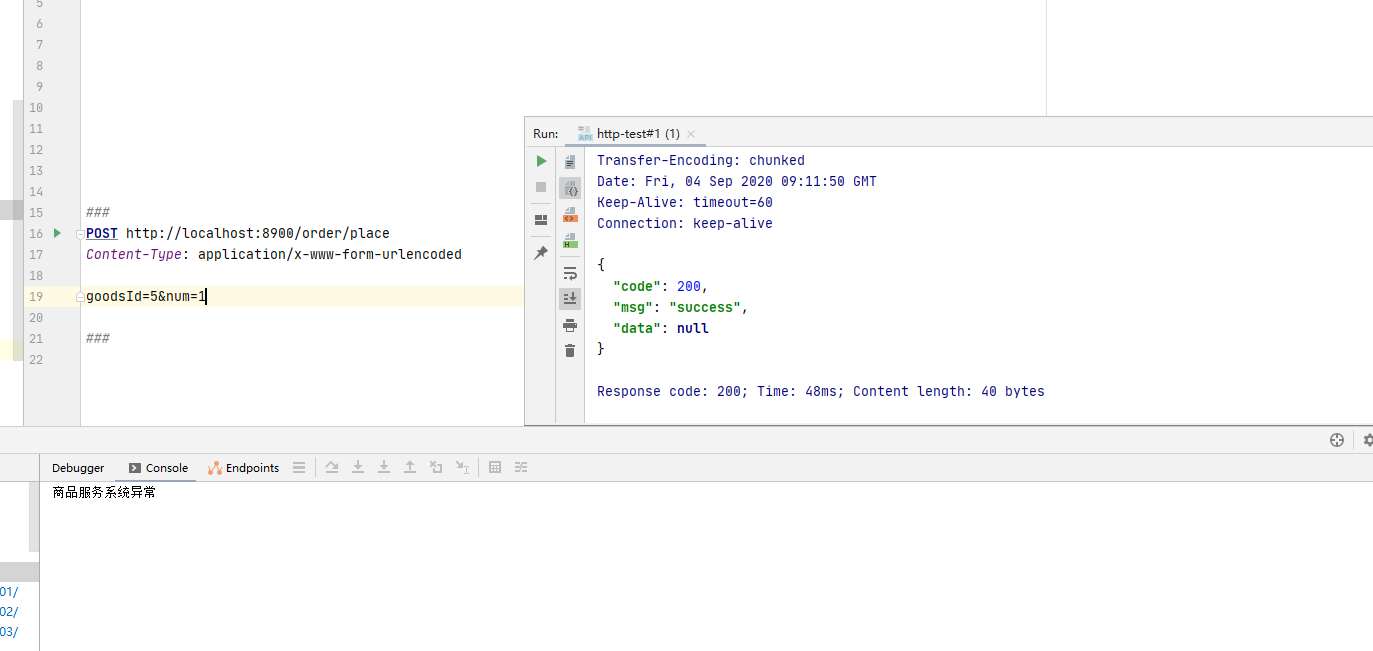
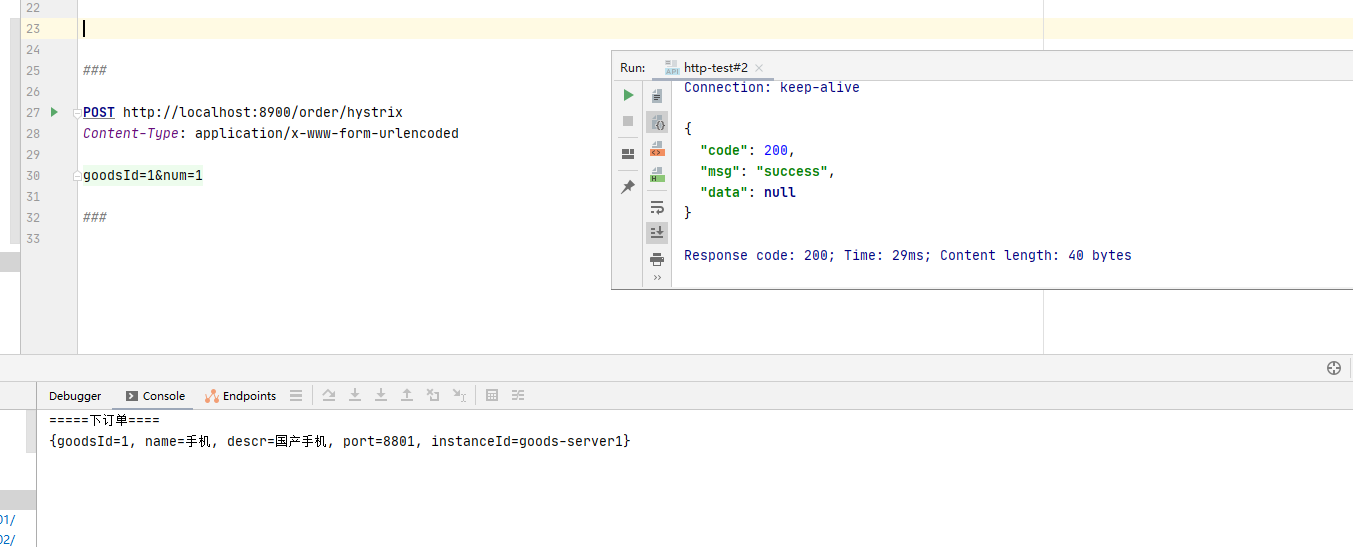
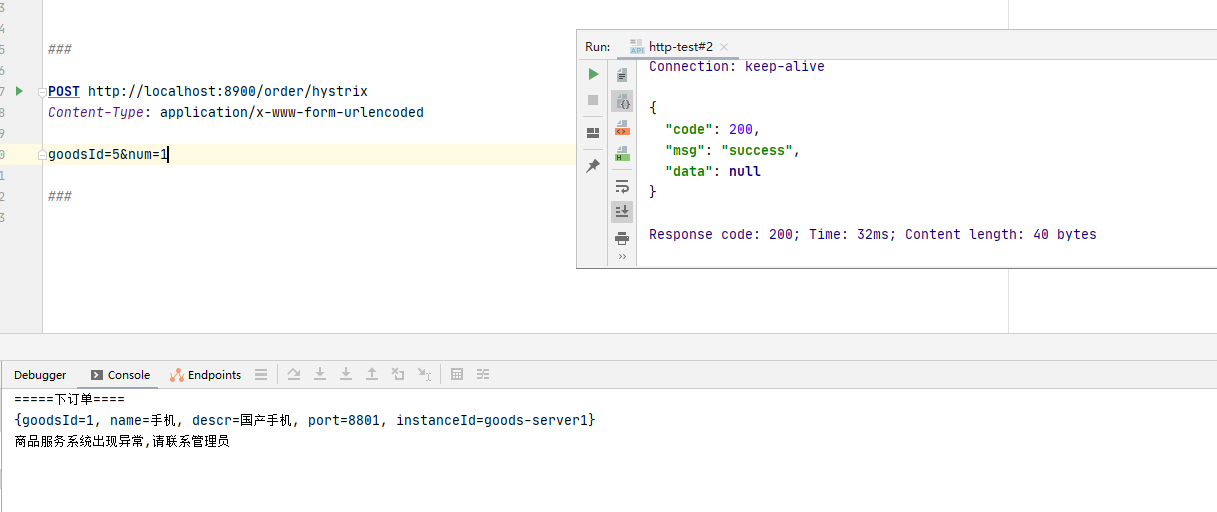
3.6 熔断测试 我们首先演示没有开启熔断的功能,即先把上边的 @EnableCircuitBreaker 注解进行注释。
下面,我们再将 @EnableCircuitBreaker 注解的注释放开,运行结果如下:
从图中可知,虽然请求了一个 goodsId 不存在的商品,但是调用方(order-server)开启了熔断机制,执行默认方法,从而使接口能正常通信而不是抛出调用方不可处理的异常导致整个系统不能正常运行。
看到这里,或许会有读者产生一个疑问,如果类中定义 N 个方法,是不是意味着同时也要定义 N 个异常处理的方法呢,答案是否定的。
Hystrix 还提供了 @DefaultProperties 统一处理请求熔断,在该注解上设置 defaultFallback 属性值,即熔断开启后要执行的方法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 @DefaultProperties(defaultFallback = "defaultByHystrix") @Service public class OrderServiceImpl implements OrderService { @Autowired private RestTemplate restTemplate; @HystrixCommand @Override public Result placeOrder(Order order) throws Exception { Result result = this.restTemplate.getForObject("http://GOODS-SERVER/goods/goodsInfo/" + order.getGoodsId(), Result.class); if (result != null && result.getCode() == 200) { System.out.println("=====下订单===="); System.out.println(result.getData()); } else { System.out.println(result.getMsg()); } return result; } public Result defaultByHystrix() { System.out.println("商品服务系统异常"); return Result.fail(500, "商品服务系统出现异常,请联系管理员"); } }
注意:defaultFallback 定义的方法必须是无参的,但是返回值必须与报错的方法返回一致。
四、服务降级 4.1 定义 Fallback 在 common-api 项目中:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 @Component public class GoodsServiceClientFallbackFactory implements FallbackFactory<GoodsServiceClient> { @Override public GoodsServiceClient create(Throwable throwable) { return new GoodsServiceClient() { @Override public Result goodsInfo(String goodsId) { return Result.fail(500, "商品服务系统出现异常,请联系管理员"); } }; } }
使用单独的类处理异常逻辑,当与服务端无法正常通信时调用此类中的方法返回结果。
4.2 修改 Feign 客户端 1 2 3 4 5 @FeignClient(value="GOODS-SERVER", fallbackFactory = GoodsServiceClientFallbackFactory.class) public interface GoodsServiceClient { @RequestMapping("/goods/goodsInfo/{goodsId}") public Result goodsInfo(@PathVariable("goodsId") String goodsId); }
4.3 开启服务降级功能 在 order-server 项目中:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 server: port: 8900 spring: application: name: Order-Web eureka: instance: instance-id: order-web prefer-ip-address: off client: register-with-eureka: false fetch-registry: true service-url: defaultZone: http://eureka01:9001/eureka/,http://eureka02:9002/eureka/ feign: hystrix: enabled: true
4.4 去掉 @HystrixCommand 配置 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 @Service public class OrderServiceImpl implements OrderService { @Autowired private GoodsServiceClient goodsServiceClient; @Override public Result placeOrderHystrix(Order order) throws Exception { Result result = this.goodsServiceClient.goodsInfo(order.getGoodsId()); if (result != null && result.getCode() == 200) { System.out.println("=====下订单===="); System.out.println(result.getData()); } else { System.out.println(result.getMsg()); } return result; } }
4.5 测试服务降级 在启动类上加 FallbackFactory 类的包扫描目录:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 @EnableCircuitBreaker @EnableFeignClients(basePackages = {"com.wno704.cloud"}) @EnableEurekaClient @SpringBootApplication public class OrderServerApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(OrderServerApplication.class, args); } }
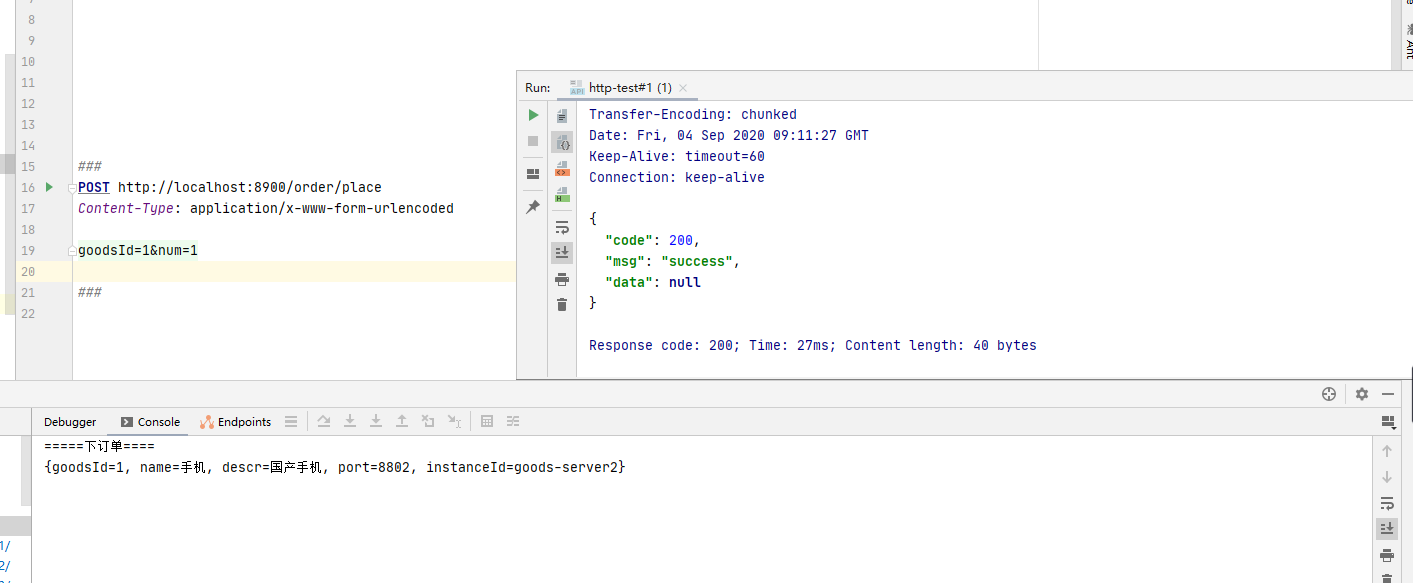
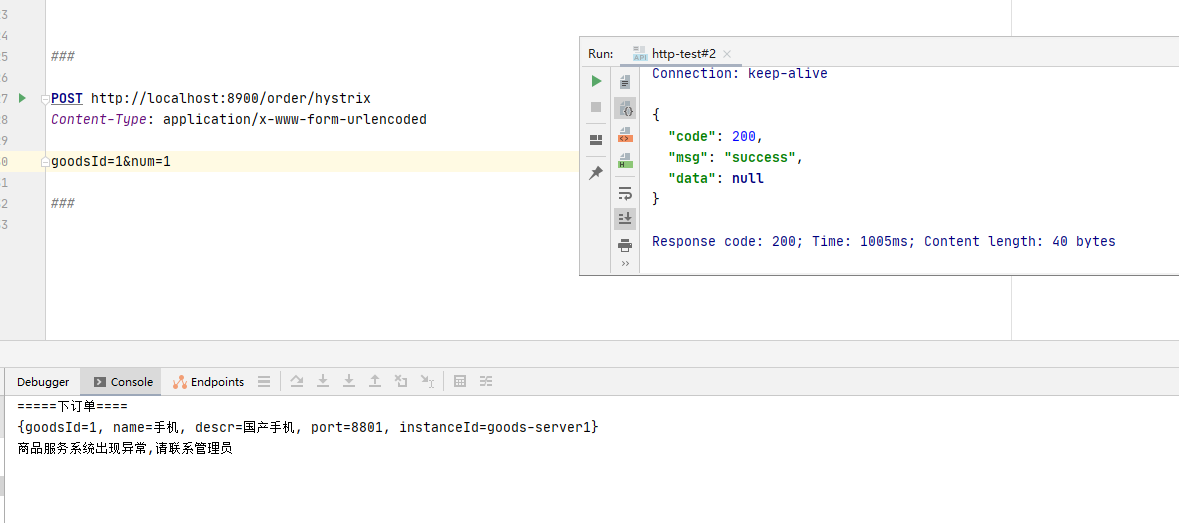
打开 idea 请求下单接口,结果如下图:
我们手动关闭 2 个商品服务,保留一个商品服务并多次请求商品服务接口,从而出模拟商品服务超过预定荷载情景,最终看到图中服务降级功能。当有请求再次访问商品服务时默认返回 GoodsServiceClientFallbackFactory 中定义的内容。
五、@HystrixCommand详解 @HystrixCommand注解还包含许多别的属性功能,下面介绍一些常用的属性配置。
5.1 服务降级 3.4 设置熔断策略中的placeOrder中我们用@HystrixCommand注解指定了服务降级方法defaultByPlaceOrder。如果placeOrder方法也抛出异常,那么我们可以再次使用@HystrixCommand注解指定placeOrder方法降级的方法,比如定义一个defaultByPlaceOrder2方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 @HystrixCommand(fallbackMethod = "defaultByPlaceOrder2"}) @Override public Result placeOrder(Order order) throws Exception { Result result = this.restTemplate.getForObject("http://GOODS-SERVER/goods/goodsInfo/" + order.getGoodsId(), Result.class); if (result != null && result.getCode() == 200) { log.info("=====下订单===="); System.out.println(result.getData()); } else { System.out.println(result.getMsg()); } return result; } public Result defaultByPlaceOrder2(Order order) { System.out.println("商品服务系统异常"); return Result.fail(500, "商品服务系统出现异常,请联系管理员"); }
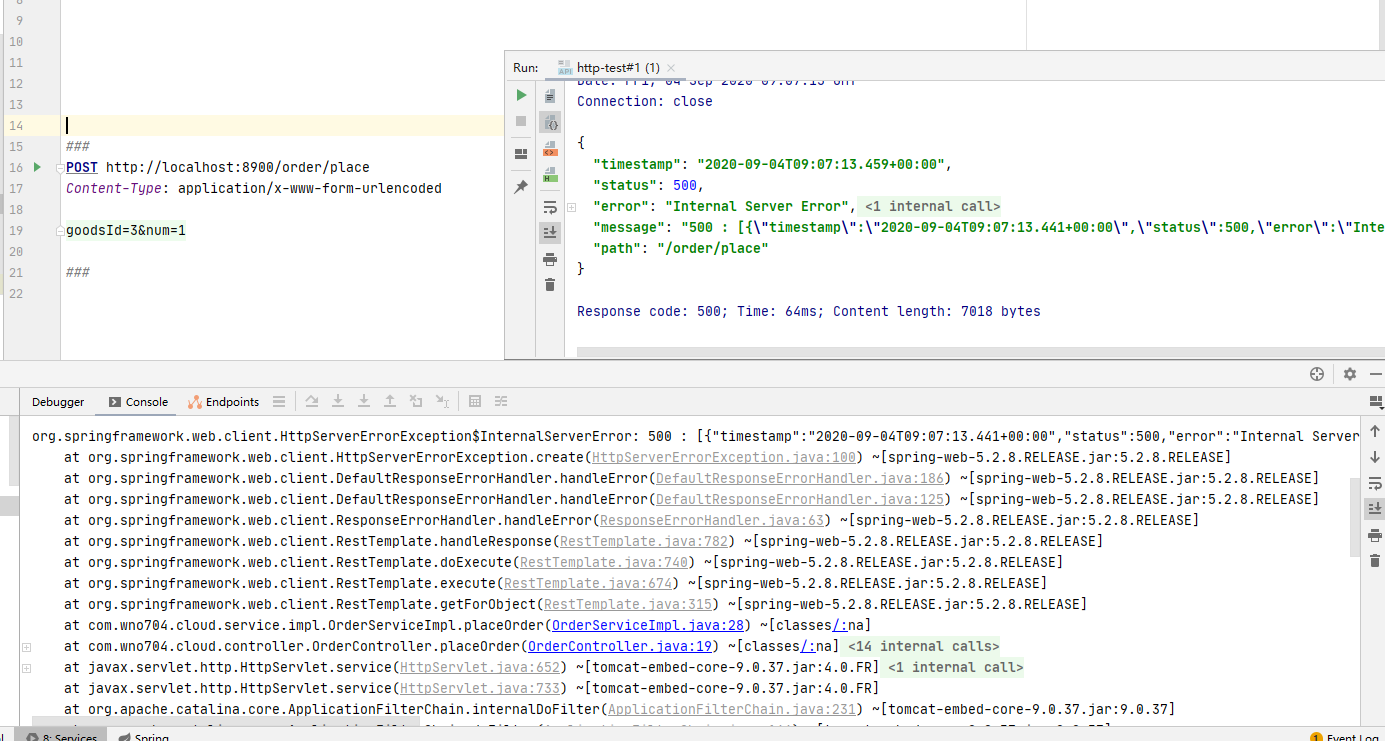
重启order-server,访问 http://localhost:8900/order/place ,我们可以获取一个不存在的goodsId
5.2 异常处理 在使用@HystrixCommand注解标注的方法中,除了HystrixBadRequestException异常外,别的异常都会触发服务降级。假如我们想指定某个异常不触发服务降级,可以使用@HystrixCommand注解的ignoreExceptions属性进行忽略。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 @HystrixCommand(fallbackMethod = "defaultByPlaceOrder2"}) @Override public Result placeOrder(Order order) throws Exception { Result result = this.restTemplate.getForObject("http://GOODS-SERVER/goods/goodsInfo/" + order.getGoodsId(), Result.class); if (result != null && result.getCode() == 200) { log.info("=====下订单===="); System.out.println(result.getData()); } else { System.out.println(result.getMsg()); } return result; } public Result defaultByPlaceOrder2(Order order, Throwable e) { System.out.println("商品服务系统异常"); return Result.fail(500, "商品服务系统出现异常,请联系管理员"); }
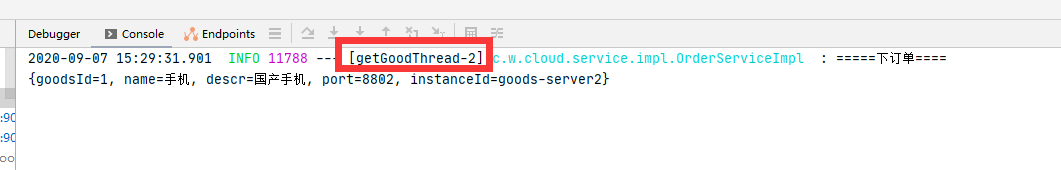
5.3 命名与分组 通过指定@HystrixCommand注解的commandKey、groupKey以及threadPoolKey属性可以设置命令名称、分组以及线程池划分,如:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 @HystrixCommand(fallbackMethod = "defaultByPlaceOrder2",ignoreExceptions = {NullPointerException.class}, commandKey = "placeOrderByGoodId", groupKey = "orderGroup",threadPoolKey = "getGoodThread") @Override public Result placeOrder(Order order) throws Exception { Result result = this.restTemplate.getForObject("http://GOODS-SERVER/goods/goodsInfo/" + order.getGoodsId(), Result.class); if (result != null && result.getCode() == 200) { log.info("=====下订单===="); System.out.println(result.getData()); } else { System.out.println(result.getMsg()); } return result; }
上面的配置指定了命令的名称为placeOrderByGoodId,组名为orderGroup,线程池名称为getGoodThread。
通过设置命令组,Hystrix会根据组来组织和统计命令的告警、仪表盘等信息。默认情况下,Hystrix命令通过组名来划分线程池,即组名相同的命令放到同一个线程池里,如果通过threadPoolKey设置了线程池名称,则按照线程池名称划分。
当placeOrder方法被调用时,日志打印如下:
5.4 Hystrix缓存 5.4.1 开启缓存 要在Hystrix中开启缓存很简单,只需使用@CacheResult注解即可,新增OrderServiceImpl的placeOrderCache方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 public String getCacheKey(String goodsId) { return goodsId; } @CacheResult(cacheKeyMethod = "getCacheKey") @Override public Result placeOrderCache(@CacheKey("goodsId") Order order) throws Exception { Result result = this.restTemplate.getForObject("http://GOODS-SERVER/goods/goodsInfo/" + order.getGoodsId(), Result.class); if (result != null && result.getCode() == 200) { log.info("=====下订单===="); System.out.println(result.getData()); } else { System.out.println(result.getMsg()); } return result; }
我们也可以明确的指定缓存的key值是什么。指定key的值有两种方式:
@CacheResult(cacheKeyMethod = "getCacheKey")
也可以指定参数对象内部属性为key值:
@CacheResult(cacheKeyMethod = "getCacheKey")
2.通过方法来指定,方法的返回值必须是String类型:
值得注意的是,方法2的优先级比方法1高。
5.4.2 缓存清除 在涉及到更新User信息的方法上,我们要及时的清除相应的缓存,否则将会导致缓存数据和实际数据不一致的问题。我们在UserService的updateUser方法上做缓存清除操作:
@CacheRemove(cacheKeyMethod = "getCacheKey")
@CacheRemove的commandKey属性和getUser里定义的一致。