一、前言 在Shiro中加入缓存可以使权限相关操作尽可能快,避免频繁访问数据库获取权限信息,因为对于一个用户来说,其权限在短时间内基本是不会变化的。Shiro提供了Cache的抽象,其并没有直接提供相应的实现,因为这已经超出了一个安全框架的范围。在Shiro中可以集成常用的缓存实现,这里介绍基于Redis和Ehcache缓存的实现。
在 《Spring-Boot-shiro权限控制》 中,当用户访问”获取用户信息”、”新增用户”和”删除用户”的时候,后台输出了三次打印信息,如下所示:
用户wno704获取权限-----ShiroRealm.doGetAuthorizationInfo
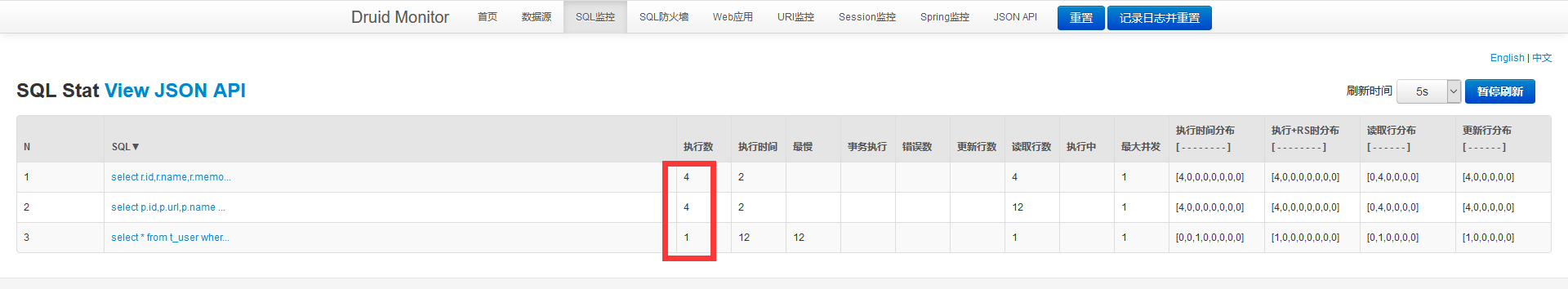
说明在这三次访问中,Shiro都会从数据库中获取用户的权限信息,通过Druid数据源SQL监控后台也可以证实这一点:
二、Redis缓存 2.1 引入Redis依赖 网络上已经有关于Shiro集成Redis的实现,我们引入即可:
1 2 3 4 5 6 <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.crazycake/shiro-redis --> <dependency> <groupId>org.crazycake</groupId> <artifactId>shiro-redis</artifactId> <version>3.3.1</version> </dependency>
2.2 配置Redis 我们在application.yml配置文件中加入Redis配置:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 spring: redis: host: 127.0.0.1 port: 10007 password: jedis: pool: max-active: 8 max-wait: -1 max-idle: 8 min-idle: 0 timeout: 0
2.3 配置Redis 接着在ShiroConfig中配置Redis:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 @Value("${spring.redis.host}") private String redisHost; @Value("${spring.redis.port}") private String redisPost; @Value("${spring.redis.timeout}") private int redisTimeout; @Value("${spring.redis.password}") private String redisPassword; public RedisManager redisManager() { RedisManager redisManager = new RedisManager(); redisManager.setHost(redisHost+":"+redisPost); redisManager.setTimeout(redisTimeout); if(!(redisPassword==null||redisPassword.equals(""))){ redisManager.setPassword(redisPassword); } return redisManager; } public RedisCacheManager cacheManager() { RedisCacheManager redisCacheManager = new RedisCacheManager(); redisCacheManager.setRedisManager(redisManager()); return redisCacheManager; }
2.4 注入RedisManager 上面代码配置了RedisManager,并将其注入到了RedisCacheManager中,最后在SecurityManager中加入RedisCacheManager:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 @Bean public SecurityManager securityManager(){ DefaultWebSecurityManager securityManager = new DefaultWebSecurityManager(); ... securityManager.setCacheManager(cacheManager()); return securityManager; }
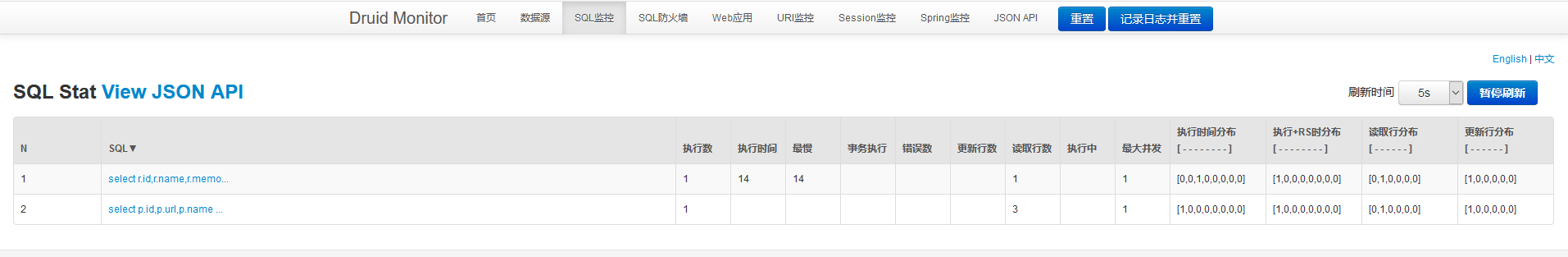
2.5 测试 配置完毕启动项目,分别访问访问”获取用户信息”、”新增用户”和”删除用户”,可发现后台只打印一次获取权限信息:
用户wno704获取权限-----ShiroRealm.doGetAuthorizationInfo
查看Druid数据源SQL监控:
三、Ehcache 3.1 Ehcache依赖 1 2 3 4 5 6 <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.shiro/shiro-ehcache --> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.shiro</groupId> <artifactId>shiro-ehcache</artifactId> <version>1.6.0</version> </dependency>
3.2 Ehcache配置 在src/main/resource/config路径下新增一个Ehcache配置——shiro-ehcache.xml:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <ehcache xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="http://ehcache.org/ehcache.xsd" updateCheck="false"> <diskStore path="java.io.tmpdir/Tmp_EhCache" /> <defaultCache maxElementsInMemory="10000" eternal="false" timeToIdleSeconds="120" timeToLiveSeconds="120" overflowToDisk="false" diskPersistent="false" diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds="120" /> <!-- 登录记录缓存锁定1小时 --> <cache name="passwordRetryCache" maxEntriesLocalHeap="2000" eternal="false" timeToIdleSeconds="3600" timeToLiveSeconds="0" overflowToDisk="false" statistics="true" /> </ehcache>
3.3 ShiroConfig配置Ehcache 接着在ShiroConfig中注入Ehcache缓存:
1 2 3 4 5 6 @Bean public EhCacheManager getEhCacheManager() { EhCacheManager em = new EhCacheManager(); em.setCacheManagerConfigFile("classpath:config/shiro-ehcache.xml"); return em; }
3.4 注入EhCacheManager 将缓存对象注入到SecurityManager中:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 @Bean public SecurityManager securityManager(){ DefaultWebSecurityManager securityManager = new DefaultWebSecurityManager(); securityManager.setRealm(shiroRealm()); securityManager.setRememberMeManager(rememberMeManager()); securityManager.setCacheManager(getEhCacheManager()); return securityManager; }
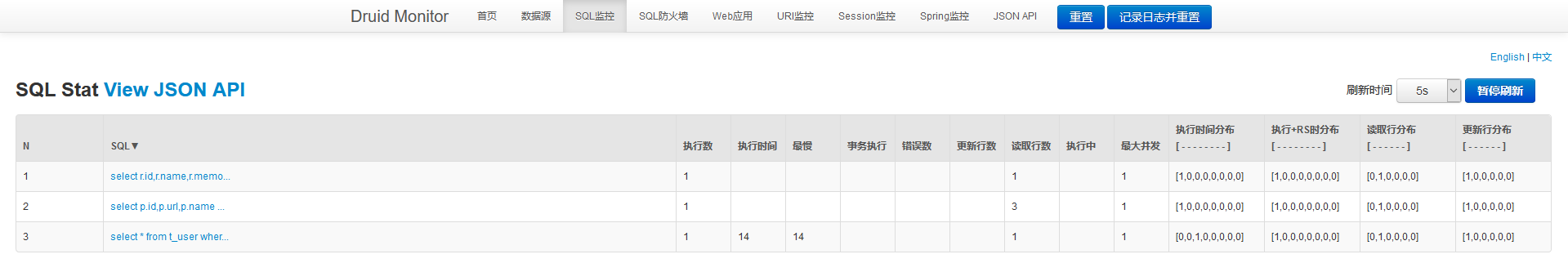
3.5 测试 配置完毕启动项目,分别访问访问”获取用户信息”、”新增用户”和”删除用户”,可发现后台只打印一次获取权限信息:
用户wno704获取权限-----ShiroRealm.doGetAuthorizationInfo
查看Druid数据源SQL监控: